Understanding the Differences between 304 Stainless and 321 Stainless Steel for Automotive Applications
304 Stainless and 321 Stainless are two common types of stainless steel alloys that differ in their chemical composition and mechanical properties. While both alloys are widely used in various industries, including the automotive industry, they have distinct differences that make them suitable for different applications.

CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
304 Stainless is a low-carbon austenitic stainless steel alloy that contains chromium (18%) and nickel (8%) as its main alloying elements. It is the most commonly used stainless steel alloy due to its good corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, and low cost.
321 Stainless is a stabilized austenitic stainless steel alloy that contains chromium (17%-19%), nickel (9%-12%), and titanium (5x[C]+0.7%) as its main alloying elements. Titanium is added to the alloy to stabilize it at high temperatures, making it more resistant to intergranular corrosion and sensitization.
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
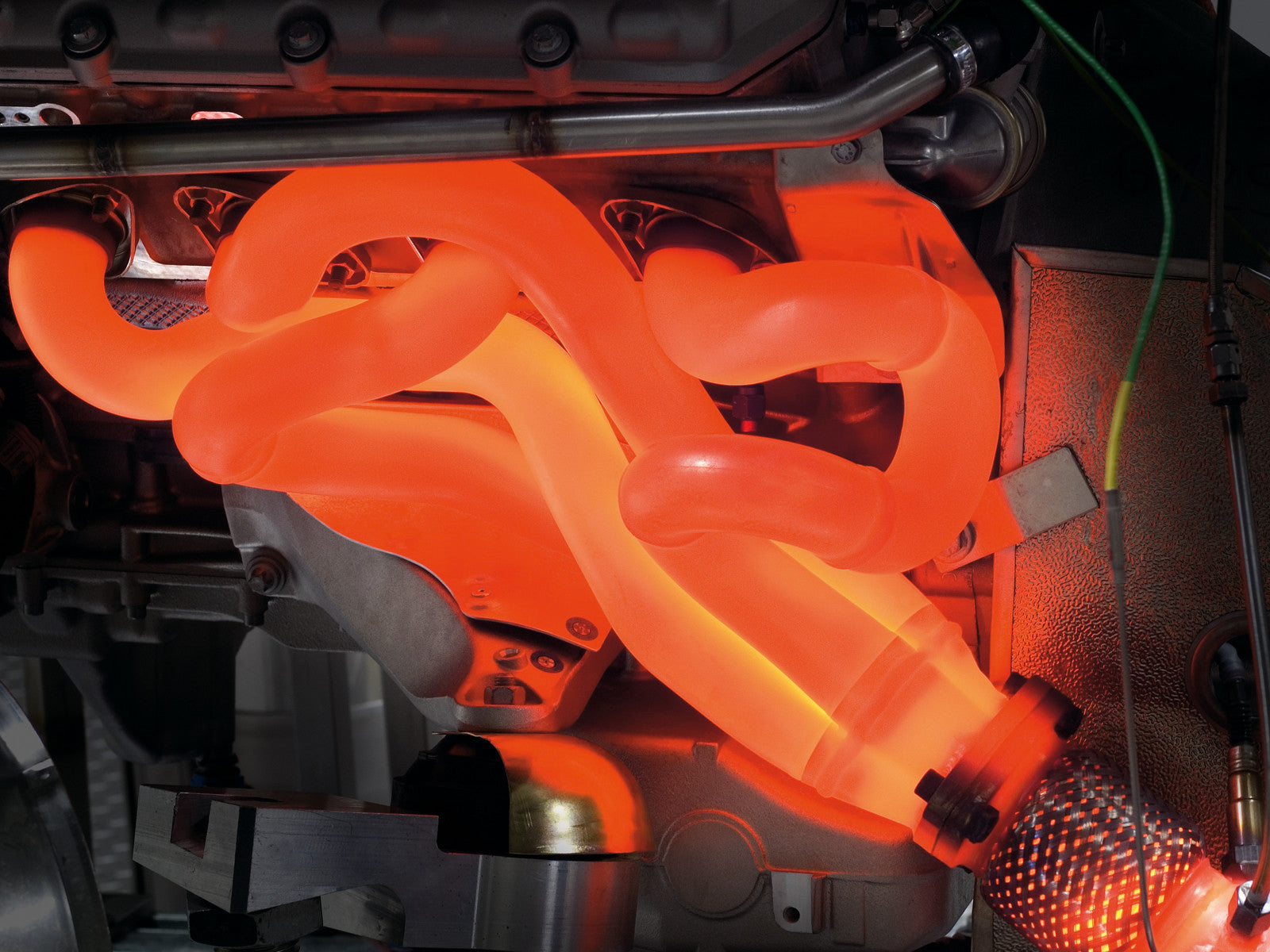
304 Stainless has excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and high strength. It has a maximum operating temperature of around 1472°F and a maximum strength of around 90 ksi.
321 Stainless has similar corrosion resistance, formability, and strength as 304 Stainless, but it is more resistant to high-temperature oxidation and creep. It has a maximum operating temperature of around 1580°F and a maximum strength of around 95 ksi.

AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS
304 Stainless is commonly used in exhaust systems, catalytic converters, and mufflers due to its good corrosion resistance and low cost. 304 Stainless is suitable for most automotive applications, including turbo manifolds, where operating temperatures do not exceed 1,472°F.
321 Stainless, due to its high-temperature resistance and resistance to sensitization, is commonly used in extremely high-temperature automotive applications where operating temperatures exceed 1,472°F but remain below 1,580°F. It is also used in welding applications where the alloy needs to be stabilized to avoid sensitization and intergranular corrosion.
In conclusion, both 304 Stainless and 321 Stainless are commonly used in automotive applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and strength. However, they differ in their chemical composition and mechanical properties, which make them suitable for different applications. While 304 Stainless is commonly used applications where operating temperatures do not exceed 1,472°F, 321 Stainless is more suitable for extremely high-temperature applications due to its resistance to oxidation and creep.

Leave a comment